co2 bond angle and shape|5.2: Molecular Shape : Cebu From the BP and LP interactions we can predict both the relative positions of the atoms and the angles between the bonds, called the bond angles. Using this information, we can .
Philippine Airlines PR2140 / PAL2140 Flugdetails - Flug Iloilo City Manila. Der nationale Philippine Airlines Flug PR2140 / PAL2140 startet von Iloilo City [ILO], Philippinen und fliegt nach Manila [MNL], Philippinen.. Die geschätzte Flugzeit Iloilo City - Manila beträgt 0:51 Stunden und die Flugstrecke für den Flug Iloilo City Manila 454 .
PH0 · Geometry of Molecules
PH1 · CO2 Molecular Geometry and Bond Angles (Carbon Dioxide)
PH2 · CO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Molar Mass & Hybridization
PH3 · CO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Molar Mass
PH4 · CO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry and Hybridization
PH5 · CO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry and
PH6 · CO2 Lewis Structure, Hybridization, Molecular
PH7 · CO2 Lewis Structure,
PH8 · CO2 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry, CO2 Lewis
PH9 · CO2 (Carbon dioxide) Lewis structure
PH10 · 5.2: Molecular Shape
PH11 · 10.2: VSEPR Theory
Dry season months at a glance. November: Officially the start of the dry season in the Philippines, however, there is still a chance of typhoons as weather can be unpredictable. Average daily temp: ° F (30 .
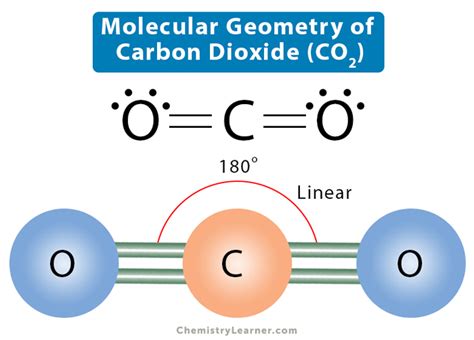
co2 bond angle and shape*******Hence CO2 has a linear molecular geometry with the bond angles of 180 degrees and symmetric distribution of electrons. Summary. To summarize this blog, we can say that Carbon Dioxide has a linear molecular geometry. It has an sp hybridization and has bond angles of 180 degrees. Tingnan ang higit pa
One needs to know the Lewis structure in order to understand the molecular geometry of any given molecule. This structure helps in knowing the arrangement . Tingnan ang higit paThe electronic configuration of the Carbon atom in its ground state is 1s22s22p2, and that of an Oxygen atom is 1s22s2p4. When the electrons are in an excited state, they jump . Tingnan ang higit paThe molecular Geometry of any compound is based on the arrangement of atoms, electron pairs, and bonds. Here in CO2, both Oxygen atoms form sigma bonds with the central carbon atom and complete their octet. As a result, there are no lone pairs of . Tingnan ang higit pa A quick explanation of the molecular geometry of CO2 including a description of the CO2 bond angles. We can see that there are only two atoms attached to the central Carbon (C) atom .From the BP and LP interactions we can predict both the relative positions of the atoms and the angles between the bonds, called the bond angles. Using this information, we can .
5.2: Molecular Shape The basic geometry is trigonal planar with 120° bond angles, but we see that the double bond causes slightly larger angles (121°), and the angle .Two double bonds connect the carbon and oxygen atoms in the CO2 Lewis structure. Each oxygen atom must bond twice, and each carbon atom must bond four times, according to the octet rule. The bond angle of CO2 is 180°. The molecular geometry of any compound can be determined by the VSEPR theory. The VSEPR chart is attached below, which will give us an idea about this. The CO2 molecule is a triatomic molecule in which carbon is covalently double bonded with oxygen on both sides where bond length is around 116.3 pm. Carbon dioxide is widely used in the food industry, oil . Bond Angles. Bond angles also contribute to the shape of a molecule. Bond angles are the angles between adjacent lines representing bonds. The bond angle .
The Lewis structure of CO2 involves two oxygen atoms sharing double bonds with a central carbon atom. As we know that, C atom has 4 valence electrons and each O atom has 6 valence electrons. The .The Lewis structure for CO2 helps us understand the bonding between the carbon and oxygen atoms and predict the molecule’s geometry, polarity, and reactivity. It also . Figure 5.9.5 5.9. 5: (a) The electron-pair geometry for the ammonia molecule is tetrahedral with one lone pair and three single bonds. (b) The trigonal pyramidal molecular structure is determined from the .
Bond angles also contribute to the shape of a molecule. Bond angles are the angles between adjacent lines representing bonds. The bond angle can help differentiate between linear, trigonal planar, tetraheral, trigonal-bipyramidal, and octahedral. The ideal bond angles are the angles that demonstrate the maximum angle where it would minimize .
This geometric shape is mainly due to the presence of a sigma bond and valence electron pairs repelling each other where they are forced to move to the opposite side of the carbon atom. As a result, the carbon atom acquires such a linear molecular shape with symmetric charge distribution. The carbon dioxide bond angle is 180 degrees.
The presence of a sigma bond and valence electron pairs repelling each other force them to move to the opposite side of the carbon atom, resulting in this geometric shape. As a result, the carbon atom takes on a linear molecular shape with symmetric charge distribution. The bond angle of carbon dioxide is 180°. Hybridization in CO 2 The Lewis structure of H 2 O indicates that there are four regions of high electron density around the oxygen atom: two lone pairs and two chemical bonds: Figure 7.6.9 7.6. 9. Thus, the electron-pair geometry is tetrahedral and the molecular structure is bent with an angle slightly less than 109.5°.
Carbon dioxide (CO 2) lewis structure has two oxygen atoms and one carbon atom. There are two double bonds around carbon atom in the CO 2. No lone pairs on carbon atom and each oxygen atom has two lone pairs on their valence shells. Shape of CO 2 is linear. Steps of drawing the lewis structure of CO 2 are explained in detail in this tutorial.Therefore, tetrahedrals have a bond angle of 109.5 degrees. How scientists got that number was through experiments, but we don't need to know too much detail because that is not described in the textbook or lecture. Using the example above, we would add that H 2 O has a bond angle of 109.5° and CO 2 would have a bond angle of 180°.
Carbon has sp3 hybridization, and the molecule takes up a tetrahedral shape to keep the repulsive forces of bonding pairs at a minimum. The bond angle of H-C-H is 109.5°. To know about the polarity of the CH4 molecule, check out our detailed blog post on CH 4 polarity to find out if the molecule is polar or nonpolar.Since the phosphorus is forming five bonds, there can't be any lone pairs. The 5 electron pairs take up a shape described as a trigonal bipyramid - three of the fluorines are in a plane at 120° to each other; the other two are at right angles to this plane. The trigonal bipyramid therefore has two different bond angles - 120° and 90°.Geometry describes how electron arrangements around that particular atom are made up of other bonds or single groups in its composition. The basic molecular geometries include: Bent, Angular, or Non-Linear. Linear. Octahedral. Pentagonal Bipyramidal. See-Saw or Distorted Tetrahedron. Square Planar. Square Pyramidal.
For the O atom in a double bond with carbon, formal charge = 6 – 0.5*4 – 4 = 6 – 2 – 4 = 0. . The shape of AX3 notation as in CO32- ion is trigonal planar with a bond angle of about 120 degrees. .
co2 bond angle and shape 5.2: Molecular Shape Shapes of Molecules. The valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR) predicts the shape and bond angles of molecules; Electrons are negatively charged and will repel other electrons when close to each other; In a molecule, the bonding pair of electrons will repel other electrons around the central atom forcing the molecule .According to the VSEPR model, the H - C - H bond angle in methane should be 109.5°. This angle has been measured experimentally and found to be 109.5°. Thus, the bond angle predicted by the VSEPR model is identical to that observed. We say that methane is a tetrahedral molecule. The carbon atom is at the center of a tetrahedron.

Carbon has 1 sigma bond each to H and N. N has one sigma bond to C, and the other sp hybrid orbital exists for the lone electron pair. Both C and N have 2 p orbitals each, set aside for the triple bond (2 pi bonds on top of the sigma). This makes HCN a Linear molecule with a 180° bond angle around the central carbon atom. CO 2 .Show the outer shell electrons only. Predict the shape of an AlCl3 molecule and the Cl−Al−Cl bond angle. (2) (iii) Aluminium chloride is used as a catalyst in the alkylation of benzene. Draw the mechanism for the reaction between benzene and chloromethane using aluminium chloride as the catalyst.Thus far, we have used two-dimensional Lewis structures to represent molecules. However, molecular structure is actually three-dimensional, and it is important to be able to describe molecular bonds in terms of their distances, angles, and relative arrangements in space (Figure 7.14).A bond angle is the angle between any two bonds that include a common .
A molecule with three electron groups orients the three groups as far apart as possible. They adopt the positions of an equilateral triangle, 120° apart and in a plane. The shape of such molecules is trigonal planar. An example is BF 3: Figure 5.4.3 5.4. 3: Boron trifluoride bonding. ( CK12 Licence)
co2 bond angle and shape Bond lengths and angles. The length of a chemical bond the distance between the centers of the two bonded atoms (the internuclear distance.)Bond lengths have traditionally been expressed in Ångstrom units, but picometers are now preferred (1Å = 10-8 cm = 100 pm.) Bond lengths are typically in the range 1-2 Å or 100-200 pm. Even .
Instagram Latest Version APK download for Android. Share Your Posts, Your Ideas, Your Stories And Stay Connected.
co2 bond angle and shape|5.2: Molecular Shape